- Cooler dryer is overly saturated
- Moisture in the cooling system freezes at the cooler expansion valve orifice and blocks circulation of the refrigerant gas
| Last Modified: 02-14-2025 | 6.11:8.1.0 | Doc ID: RM100000001FPE3 |
| Model Year Start: 2019 | Model: RAV4 | Prod Date Range: [11/2018 - ] |
| Title: HEATING / AIR CONDITIONING: AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM (for Gasoline Model): ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION; 2019 - 2025 MY RAV4 [11/2018 - ] | ||
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
PROCEDURE
1. COOLING PERFORMANCE TEST
(a) Install the air conditioning tool set to the vehicle.
(b) Set the vehicle to the following conditions. [*1]
|
Item |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
Vehicle Body |
Vehicle stopped in shade |
|
Door |
Fully open |
|
A/C Switch |
ON |
|
Fresh/recirculation Mode Control Damper Position |
Recirculation |
|
Air Vent Damper Position |
FACE |
|
Set Temperature |
MAX COLD |
|
Blower Speed |
HI |
|
Air Conditioning Air Inlet Temperature*2 |
25 to 34°C (77 to 93.2°F) |
|
Condenser Pressure (Gauge High Pressure Side)*3 |
1.37 to 1.57 MPaG (14 to 16 kgf/cm2) |
HINT:
*2: This inspection can be judged correctly only if the air inlet temperature is within a range of 25 to 34°C (77 to 93.2°F). Therefore, postpone the test if the temperature is low.
If the condenser pressure (gauge high pressure side) is high, splash the condenser with water to lower the pressure. Conversely, if the condenser pressure is low, cover the front of the condenser to raise the pressure.
(c) Place a wet and dry bulb thermometer at the air inlet (necessary for measuring the humidity), and insert its dry bulb at the center of the air vent to measure.
(d) Operate the air conditioning in the conditions of [*1], and allow the temperature at the air vent to stabilize. (Approximately 5 to 6 minutes)
(e) Measure the wet and dry temperatures of the air inlet and the temperature of the air vent.
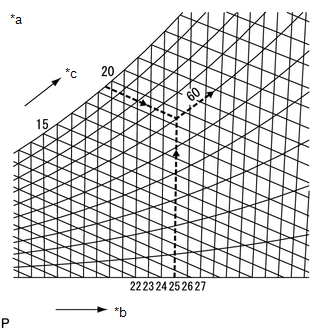
(f) Map the measurement values of the air inlet to the psychometric diagram to find the relative humidity.
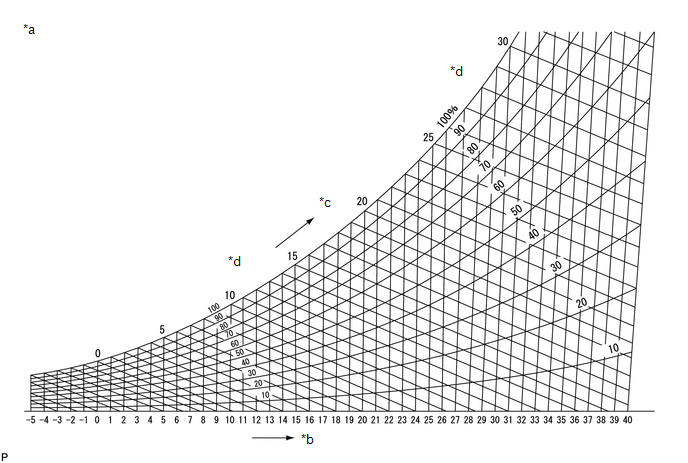
|
*a |
Psychrometric Diagram |
*b |
Dry Bulb Temperature (°C) |
|
*c |
Wet Bulb Temperature (°C) |
*d |
Relative Humidity (%) |
|
(1) One way of finding the relative humidity is to find the intersection point of the wet and dry bulb temperatures, 19.5°C and 25°C, respectively, of the wet and dry bulb thermometer set at the air inlet. In this case, the relative humidity is 60%. |
|
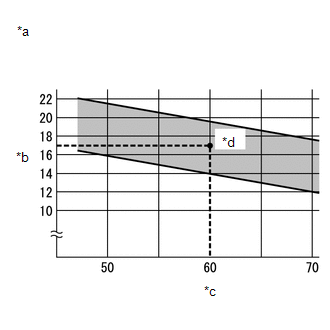
(g) Check the cooling performance by mapping the relative humidity and the difference between the measured dry bulb temperatures of the air inlet and air vent in the standard performance chart.
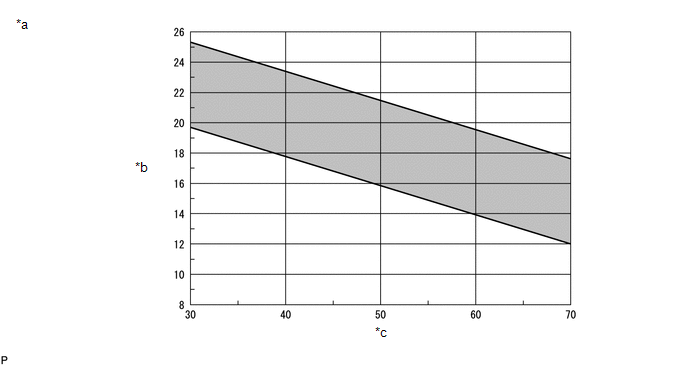
|
*a |
Standard Performance Chart |
*b |
Air Inlet/air Vent Temperature Difference (°C) |
|
*c |
Relative Humidity (%) |
- |
- |
Standard:
Must be within the range between the diagonal lines in the chart.
|
(1) One example of how to check the cooling performance using a standard performance chart is to find the intersection point of the relative humidity (60%) and the difference in dry bulb temperatures at the air inlet and vent (17°C). In this example, the cooling performance is inside the standard range. |
|
2. CHECK REFRIGERANT GAS PRESSURE
(a) Check refrigerant pressure using gauge.
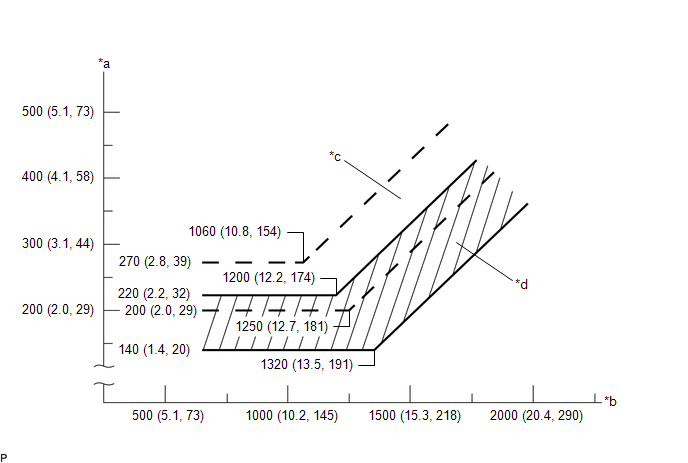
|
*a |
Pressure on Low Pressure Side kPa (kgf/cm2, psi) |
*b |
Pressure on High Pressure Side kPa (kgf/cm2, psi) |
|
*c |
Blower High Zone |
*d |
Blower Low Zone |
(1) Install the air conditioning tool set.
(2) Set the vehicle to the following conditions. [*3]
Measurement Condition:
|
Item |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
Vehicle Condition |
Engine running |
|
Doors |
Fully closed (windows also fully closed) |
|
A/C Switch |
On |
|
Recirculation/fresh Control Switch |
Recirculation |
|
Set Temperature |
MAX COLD |
|
Blower Speed |
HI |
|
Air Conditioning Air Inlet Temperature |
25 to 35°C (77 to 95°F) |
(3) In conditions [*3], read the gauge and check the numerical value.
-
Normal
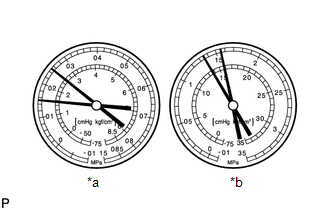
*a
LO
*b
HI
Specified Condition:
Gauge Reading
Pressure Side
Refrigerant Volume
Low
150 to 250 kPa (1.5 to 2.5 kgf/cm2, 22 to 36 psi)
High
1370 to 1570 kPa (14.0 to 16.0 kgf/cm2, 199 to 228 psi)
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when the refrigerant gas volume is normal.
-
During malfunction
-
Symptom 1: During cooling operation, pressure on low pressure side cycles between normal and vacuum.
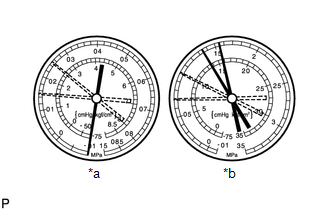
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptom
The air conditioning system works intermittently
Cause
Moisture in the cooling system freezes at the cooler expansion valve orifice and temporarily prevents refrigerant gas from circulating. The condition, however, is restored to normal after the ice is melted.
Diagnosis
Action Taken
- Replace the cooler dryer
- Remove moisture from cycle by repeatedly evacuating air
- Add an appropriate volume of new refrigerant gas
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when moisture has gotten into the cooling system.
-
Symptom 2: The pressure on both the low and high pressure sides is low.
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
- Cooling is not working well
- Coolant performance is insufficient
Cause
There is a gas leak somewhere in the cooling system
Diagnosis
- Insufficient refrigerant gas volume
- Refrigerant gas leak
Action Taken
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when cooling is not working well.
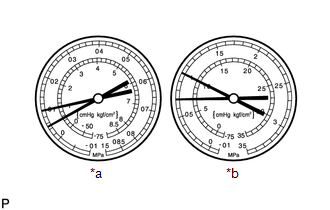
*a
LO
*b
HI
-
Symptom 3: The pressure on both the low and high sides is low, which causes condensation on the pipe from the cooler condenser assembly to the A/C unit.
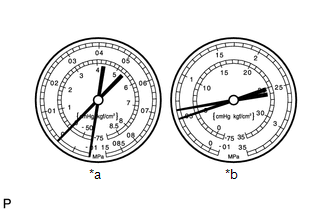
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
Cooling is not working well
Cause
Dust in the cooler condenser core blocks the flow of refrigerant gas
Diagnosis
Blockage of cooler condenser core
Action Taken
Replace the cooler condenser assembly
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when cooling by refrigerant gas is not working well.
-
Symptom 4: The pressure on both the low and high sides is low, which causes frost or condensation on the pipe before and after the cooler condenser core or cooler expansion valve.
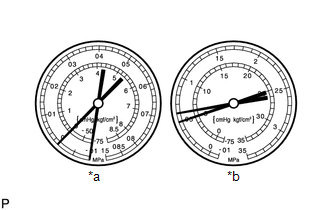
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
Cooling is not functioning (also functioning occasionally)
Cause
- The flow of refrigerant gas is blocked by moisture or dust in the cooling system
- The flow of refrigerant gas is impaired by refrigerant gas leak from the cooler expansion valve
Diagnosis
Refrigerant gas cannot circulate
Action Taken
- Check the cooler expansion valve
- Remove dust in the cooler expansion valve with an air gun
- Replace the cooler condenser assembly
- Evacuate the air conditioning system, and then add an appropriate volume of new refrigerant gas
- If there is a refrigerant gas leak from the cooler expansion valve, replace the valve
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when refrigerant gas does not circulate.
-
Symptom 5: The pressure on both the low and high pressure sides is high.
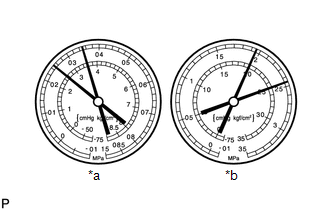
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
Cooling is not working well
Cause
- The flow of refrigerant gas is blocked by moisture or dust in the cooling system
- The flow of refrigerant gas is impaired by refrigerant gas leak from the cooler expansion valve
Diagnosis
- Excessive refrigerant gas volume
- Cooling of cooler condenser core is insufficient
Action Taken
- Clean the cooler condenser core fin
- Check the operation of the condenser fan
- Adjust the refrigerant gas volume
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when the refrigerant gas volume is excessive or cooling of the cooler condenser core is insufficient.
-
Symptom 6: The pressure on both the low and high pressure sides is high, and the low pressure line is too hot to touch.
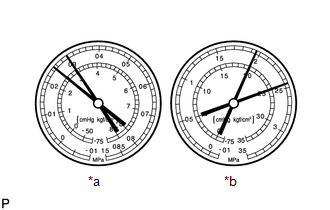
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
Cooling is not functioning
Cause
Air in refrigeration system
Diagnosis
- Air is in the refrigeration system
- Evacuation of the air conditioning system is insufficient
Action Taken
- Check if the compressor oil is dirty or insufficient
- Evacuate the air conditioning system, and then add an appropriate volume of new refrigerant gas
HINT:
- Notes: The gauge indicates when the cooling system is open without the system being evacuated and filled with refrigerant gas.
- The illustration shows the gauges when air has gotten into the refrigerant system.
-
Symptom 7: The pressure on both the low and high pressure sides is high, and frost or condensation is forming on the low pressure side.
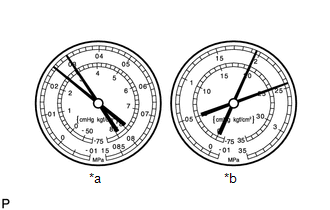
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
Cooling is not working well
Cause
Trouble with the cooler expansion valve
Diagnosis
- Refrigerant gas volume is excessive on the low pressure pipe line
- Cooler expansion valve opened too far
Action Taken
Replace the cooler expansion valve
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when the cooler expansion valve is improper.
-
Symptom 8: The pressure on the low pressure side is high and the pressure on the high pressure side is low.
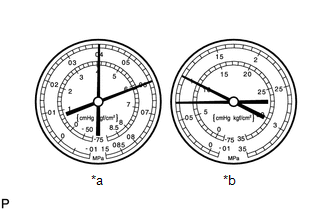
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
Cooling is not functioning
Cause
Compression leak inside the compressor with pulley assembly
Diagnosis
- Compression malfunction
- Valve leak or damaged sliding parts
Action Taken
Repair or replace the compressor with pulley assembly
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when the compression in the compressor with pulley assembly is poor.
-
Symptom 9: The pressure is the same on both the low and high pressure sides.
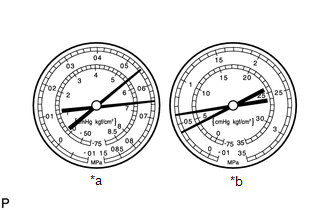
*a
LO
*b
HI
Standard Value Measurement Result
Symptoms
Cooling is not functioning
Cause
Trouble with the compressor with pulley assembly
Diagnosis
Compressor with pulley assembly does not rotate
Action Taken
Repair or replace the compressor with pulley assembly
HINT:
The illustration shows the gauges when the compressor with pulley assembly is malfunctioning.
-
Symptom 1: During cooling operation, pressure on low pressure side cycles between normal and vacuum.
3. CHECK COOLER CONDENSER ASSEMBLY
(a) When the fins of the cooler condenser assembly are dirty, clean with water and dry with compressed air.
NOTICE:
- Do not damage the cooler condenser assembly fins.
- When the cooler condenser assembly fins are bent, use a screwdriver or pliers to straighten them.
4. CHECK FOR REFRIGERANT GAS LEAK
(a) Using a halogen leak detector, check for refrigerant gas leaks from connections on the pipe line.
(b) If refrigerant gas is leaking from a connection on the pipe line, check the tightening torque of the joint.
5. CHECK ECO DRIVE MODE
HINT:
Depending on the environment (condition), the actual control may not change in some situations even if ECO drive mode is activated.
(a) Check that the indicator illuminates and airflow volume from the air outlet is controlled when the integration control and panel assembly (ECO switch) is turned on.
(b) Check that the indicator light turns off and that airflow control is canceled when the integration control and panel assembly (ECO switch) is turned off.
|
|
|
![2019 - 2020 MY RAV4 [11/2018 - 08/2020]; HEATING / AIR CONDITIONING: REFRIGERANT LINE (for Gasoline Model): REMOVAL](/t3Portal/stylegraphics/info.gif)